-
EV Business Solutions
-
EV Drivers
-
Our Company
-
Resources
Guide On How To Charge Your Electric Car With Charging Stations
As electric vehicles (EVs) and plug-in hybrids continue to rise in popularity, owners are facing the challenge of understanding the different charging options available. This guide will provide clarity on types of EV charging, the three main charging locations, charging times, connectors, and resources to help you charge your EV efficiently.
Where You Can Charge Your EV
1) Home Charging |
Understanding the terminology related to charging stations is crucial, as terms are often used interchangeably:
- Charging Station
- Charging Outlet
- Charging Plug
- Charging Port
- Charger
- EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipement)
Feel free to share this guide on Facebook or X to spread the knowledge!
Home Charging for Electric Vehicles
Home charging is where most EV owners charge their vehicles, accounting for more than 80% of charging sessions. Understanding the different home charging options is essential for maximizing convenience and efficiency.
Home Charging Options: Level 1 & Level 2
- Level 1 Charging:
- This is the standard charger that usually comes with your EV. It plugs into a 120-volt outlet, but charges your car slowly—taking about 20 hours to fully charge and providing a range of 200 km.
- This is the standard charger that usually comes with your EV. It plugs into a 120-volt outlet, but charges your car slowly—taking about 20 hours to fully charge and providing a range of 200 km.
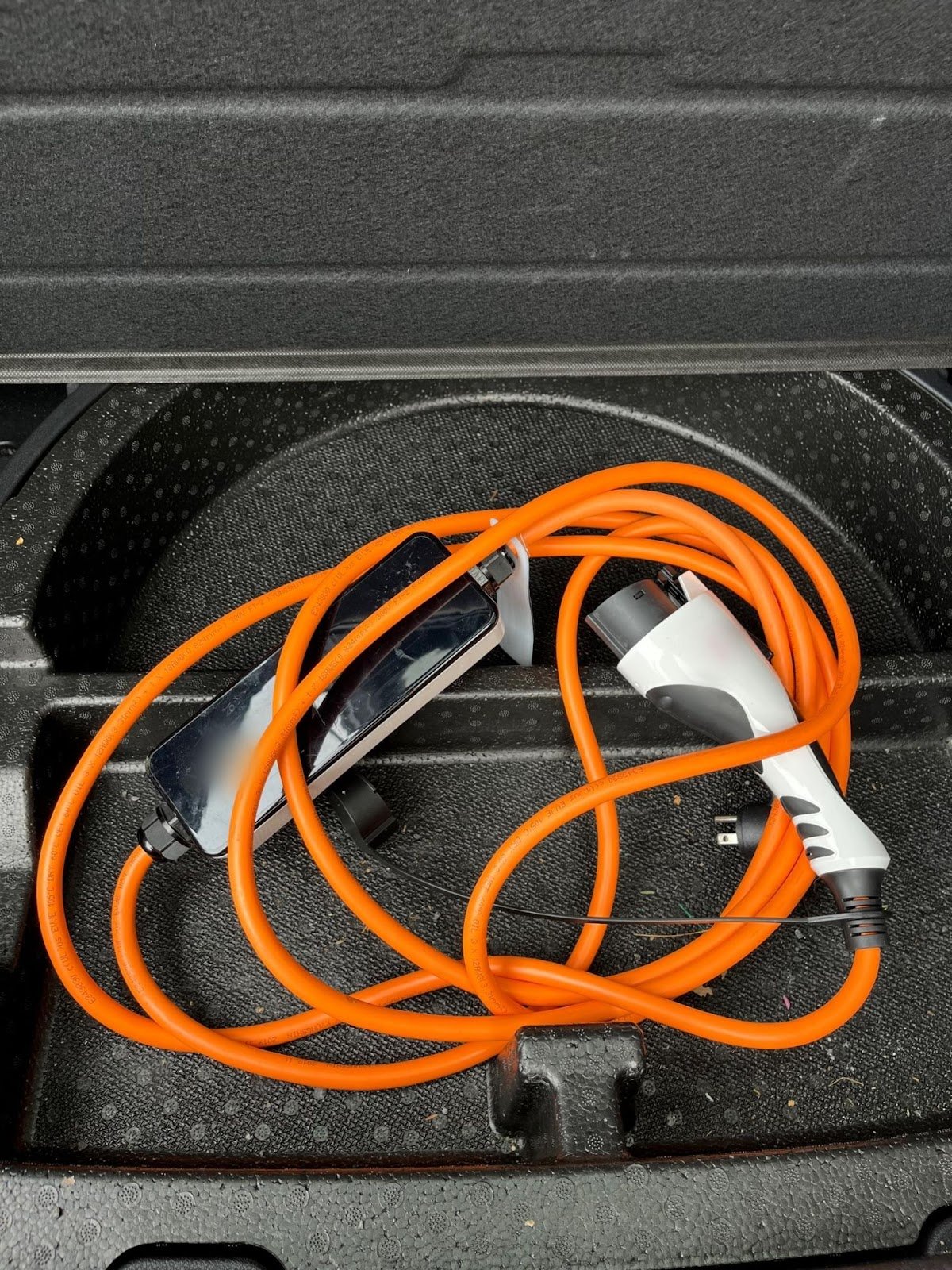

- Level 2 Charging:
- Level 2 chargers require a 240-volt outlet and can charge your EV 3 to 7 times faster, depending on the model. These chargers are generally not included with your EV purchase. All North American Level 2 chargers use the SAE J1772 connector. To explore different SAE J1772 connector models, visit our online store.
- Level 2 chargers require a 240-volt outlet and can charge your EV 3 to 7 times faster, depending on the model. These chargers are generally not included with your EV purchase. All North American Level 2 chargers use the SAE J1772 connector. To explore different SAE J1772 connector models, visit our online store.
Note: Installing a Level 2 charger may require a licensed electrician. You can find subsidies for these installations in some provinces and states—check the links below for more information:

Benefits of Home Charging
Faster Charging:
A Level 2 charger can charge your vehicle 5 to 7 times faster than a Level 1 charger. For plug-in hybrids, it’s about 3 times faster, reducing the need for public charging.
Convenience:
Charge your EV overnight at home. Simply plug in your car in the evening, and it will be ready by morning. This is especially useful since most EVs have a sufficient range for daily commutes, eliminating the need for public charging.
Cost Savings:
Home charging is more affordable than public charging or gasoline. A typical Canadian EV driver could save up to $2,500 annually on fuel and maintenance. To get the lowest electricity rates, charge during off-peak hours (e.g., 7 PM to 7 AM on weekdays). In Quebec, you can use Hydro-Québec's website to estimate savings. U.S. drivers can compare electricity and gasoline costs to see potential savings.
Public Charging for Electric Vehicles
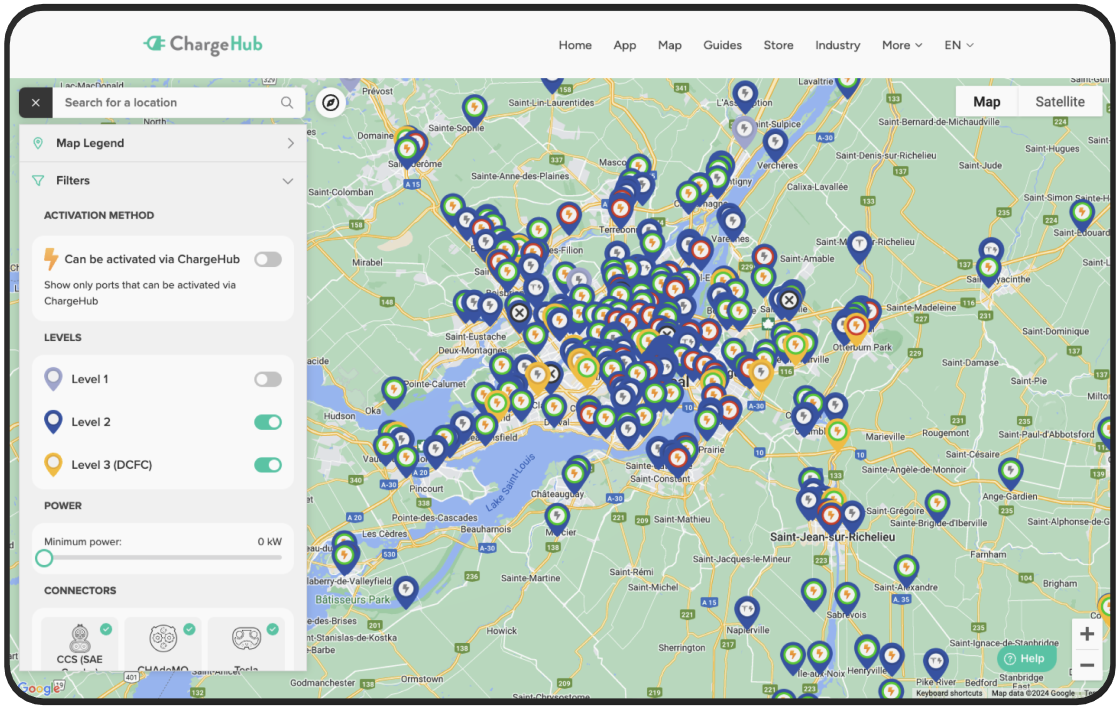
Public charging stations are essential for long trips or when your battery is running low. These stations are located near businesses like restaurants, shopping centers, and public areas. The ChargeHub map and app (available for iOS and Android) help you find charging stations and view real-time availability.
1) Charging Levels |
2) Charging Station Connectors |
Types of Charging Levels for Public Charging
There are three main charging levels:
- Level 1: Slowest option, usually takes about 20 hours for a full charge.
- Level 2: Common in public stations, providing faster charging (typically 5 to 11 hours for 200 km).
- Level 3 (DCFC): Fastest, offering 80% charge in 15 to 60 minutes depending on your vehicle’s battery capacity.
Charging Level Summary
|
Level |
ChargeHub Markers |
Power (kW) |
Approximate Charging Time (Empty Battery) |
|
1 |
|
1 |
20 hours for 200 km; 43 hours for 400 km |
|
2 |
|
3-20 |
200 km: +/- 5 hours 400 km: +/- 11 hours |
|
3 (DCFC) |
|
20-350 |
15-60 minutes for 80% charge |
Level 1:
Uses a 120-volt outlet, taking 20 hours for a full charge.

Level 2:
Equivalent to home Level 2 charging stations, typically found in public locations.

Level 3 (DCFC):
Fastest option, providing quick charging but may not be compatible with all EVs.

Which Level of Charging Should You Use?
For quick charges, Level 3 is the best choice. However, it’s only effective if your EV’s battery is below 80%. After that, the charging speed slows, and it’s better to switch to a Level 2 station to continue your journey or save on costs.
Charging Connectors
Level 1 & 2 Connectors (SAE J1772):
This connector works with all EVs in North America, with an adapter available for Tesla vehicles.
|
Connector: Port J1772 Level: 2 Compatibility: 100% of electric vehicles Tesla: With adapter |
Level 3 Connectors:
- CHAdeMO: Common for DCFC stations, but check compatibility with your EV’s specifications.
- SAE Combo CCS (Combo Charging System): Another standard for fast chargers. Tesla vehicles are generally not compatible with these connectors without an adapter.
|
Connector: CHAdeMO |
|
Connector: SAE Combo CCS |
Checking Connector Compatibility:
Before using a public charger, check that the available connectors match your EV’s requirements. Some DCFC stations may only offer CHAdeMO or SAE Combo CCS connectors, so ensure your EV supports the connector type before plugging in.
The other connector of interest to some drivers is the Tesla connector, which is only compatible with Tesla-brand cars. The Tesla connector is fitted to certain Level 2 chargers and Tesla Supercharger fast-charging stations. However, a CCS adapter is available for Tesla vehicles, so it's now possible to charge your EV at any fast-charging station. Long EV journeys have never been so easy!
Tesla-Specific Connectors:
|
Connector: Tesla HPWC |
|
Connector: Tesla supercharger |
Wall Outlet for Charging Stations:
|
Wall outlet: Nema 515, Nema 520 |
|
Wall outlet: Nema 1450 (RV plug) |
|
Wall outlet: Nema 6-50 |
EV Charging Networks
In North America, various public charging networks operate different stations. While some networks cover specific regions, ChargeHub makes it easy to use over 120,000 charging stations across North America. Our app lets you activate and pay directly without needing separate accounts for each network.
For a seamless charging experience, download the ChargeHub app and take advantage of its integrated payment system.
Charging an Electric Car at Work
Workplace charging operates similarly to home charging, with the added benefit of being available at your place of work. If your employer provides this service, you can charge your EV during your workday, potentially meeting most of your commuting needs. Depending on your employer's setup, you may find Level 1 or Level 2 charging stations in company parking lots.
The pros of workplace charging
A longer electric range
When combined with home charging, workplace charging can nearly double your EV’s daily electric range, which is very cost-effective. This is particularly beneficial for plug-in hybrid vehicles, allowing you to rely more on electric power, reducing fuel consumption.
Faster Charging with Level 2
Level 2 chargers allow quicker recharges, which is valuable if you're at work for only part of the day or if your workplace has intermittent foot traffic.
Large Savings on Transportation Costs
Some employers cover the costs of workplace charging, meaning you can charge your EV for free. Even when there is a fee, it’s typically less than public charging options.
Government Incentives for Workplace Chargers
Governments in some regions offer incentives to employers who install EV charging stations. However, many employers are not aware of these programs. Employees can help by informing them about the available incentives.
For the United States, we suggest you visit your state's government website.
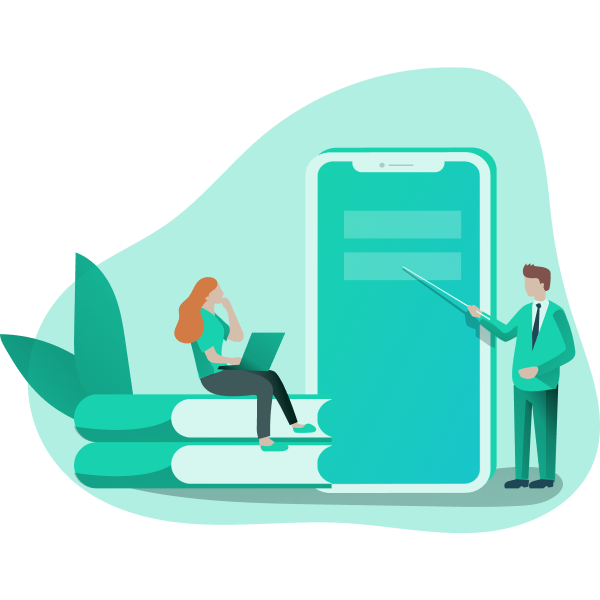
After understanding the advantages of both home and workplace charging, you may want to explore how to choose the right home charging station. Given that most of your EV charging will take place at home, it’s essential to select the right charger for your needs.






.jpg?width=840&height=560&name=Charger-Comparison%20(1).jpg)